Trade-based money laundering (TBLM) became one of the major challenges to governments and intergovernmental bodies over the last 20 years. Criminal organizations and terrorist financiers use TBLM as a way to legalize slush funds because direct “monetary” ways are well covered by financial institution policies and systems.
Post-factum detection of TBML may lead to significant damage and a corresponding increase of trade finance operations costs for enterprises and customers alike. Unfortunately, there is still no interbank solution that would allow 100% coverage of the trade finance market and every institution must build its own anti-money laundering (AML) system to prevent TBML activities of customers.
Criminal organizations and terrorist financiers use outdated but functional methods of money laundering including:
- Over-invoicing
- Under-invoicing
- Multiple-invoicing
- Over- or under-shipment
- Misrepresentation of quality
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) guide defines primary red flags for cross-border transactions that should be investigated:
- Heavy discrepancies between the description of the commodity, bill of lading, and invoice
- Heavy discrepancies between the description of the goods on the bill of lading (or invoice) and the actual goods shipped
- Heavy discrepancies between the value of the commodity reported on the invoice and the commodity’s fair market value
- Inconsistent size of the shipment compared to the scale of the exporter or importer’s regular business activities
- Commodity being shipped is designated as “high risk” for money laundering activities
- Commodity being shipped is inconsistent with the exporter or importer’s regular business activities
- Shipment does not make economic sense
- The commodity being shipped to (or from) a jurisdiction is designated as “high risk” for money laundering activities
- The commodity is being transhipped through one or more jurisdictions for no apparent economic reason
- The method of payment is inconsistent with the risk characteristics of the transaction
- The transaction involves cash or other payments from third party entities that have no connection with the transaction
- The transaction has repeated use of amended or frequently extended letters of credit
- The transaction includes the use of front or shell companies
As you see every transaction requires multi-dimensional data analysis from different internal and external data sources. Moreover, banks must not consider transactions as the atomic object of the AML process. Complex money laundering schemas may include tens of trade deals and only complex analysis of the client’s and affiliated entities, behavioristic models, correct segmentation, shipment tracking (analysis,) and market analysis may allow minimizing the probability of TBML.
Today, many banks still rely on the experience and knowledge of trade finance compliance managers. This limits the depth of compliance, and slows the pace of the application process, while creating a greater risk of human error.
Integration of artificial intelligence/machine learning (AI/ML) and big data services (even partially in AML processes) provides advanced capabilities of TBML detection to increase depth of analysis and decrease manual compliance efforts. These technologies also significantly decrease the time needed for application consideration and decrease reputational risk which leads to lower trade finance transactional and processing costs.
Based on our experience and collaboration with leading financial institutions, SoftServe has built our vision of how AI/ML and big data will help financial institutions:
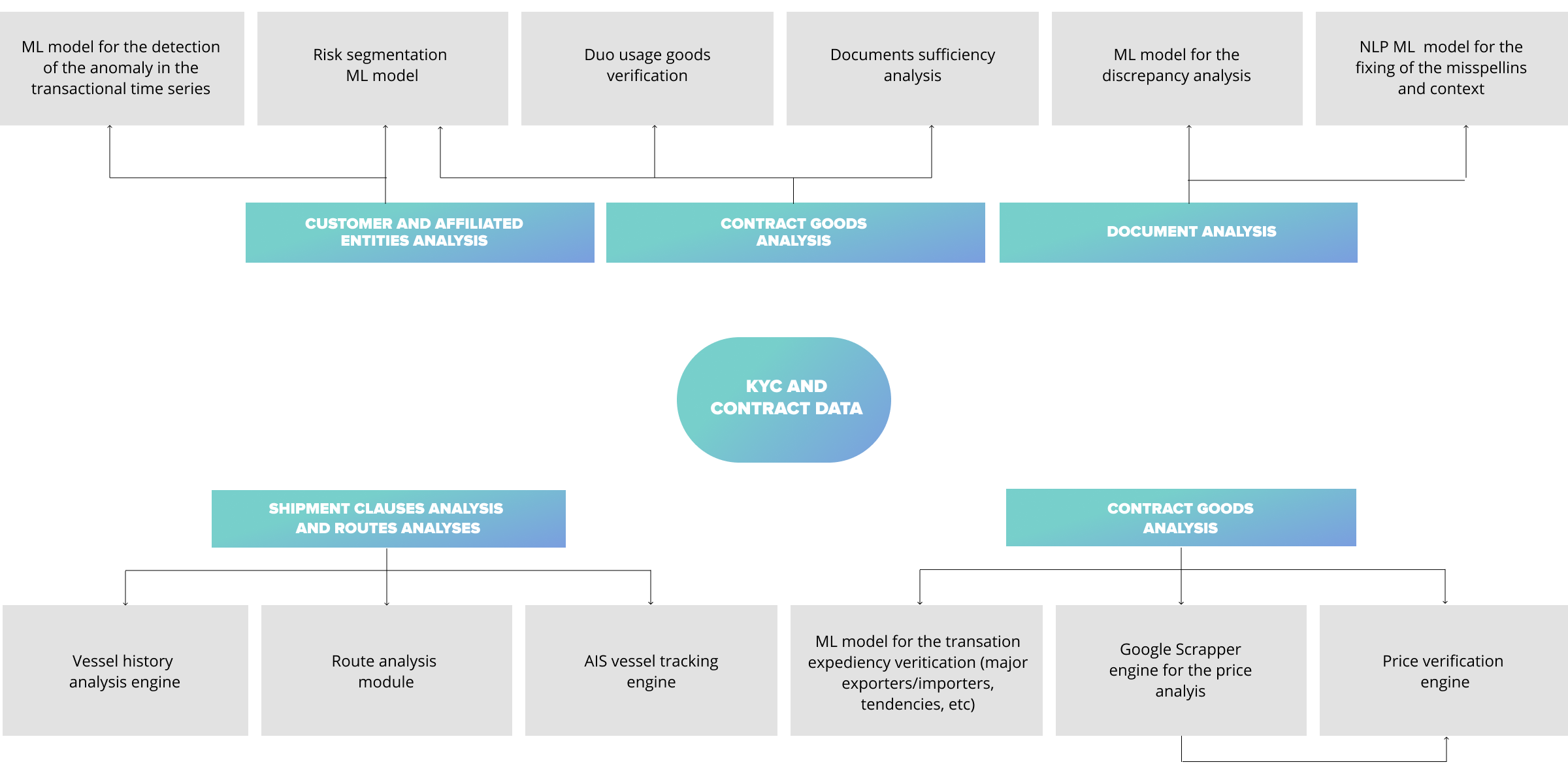
As a private advisor and services provider with over 27 years of Financial Services enterprise experience, we approach TBML prevention with a converged business and technology strategy.
Our global Business Analysis and Financial Services experts apply decades of experience and understanding of end-to-end trade finance processes including shipping management, customs brokerage and more. Simultaneously, our Intelligent Enterprise teams of big data, data science, and AI/ML experts have delivered a significant number of models and data processing platforms to automate, enhance the efficiency of all stages of the anti-TBML framework.
How does your organization prevent trade-based money laundering?
Who on your team is currently working to prevent TBML?
Do you have a strategy or are you leveraging both business and advanced technologies?
Let’s talk about your anti-TBML journey and how SoftServe can help you combat legacy technology threats with the latest in advanced solutions.

