Over the last few years, there has been active investment in decentralized currencies and mobile solutions, providing compelling alternatives to traditional money transferring systems.
Many people are asking: “What will payment and settlement solutions look like in the future?”
Our vision, which is based on a SoftServe BFSI Lab investigation, is that the future (which is now in many aspects) will be driven by competitive pressure from these innovations. The future of payments, money, and value transfers will be transformed into more global solutions. These will be faster, more transparent, and cheaper for all parties.
As we discovered, the majority of new, non-traditional schemes will be deeply integrated into the existing financial ecosystem as alternative payment networks. It triggers the appearance of new sets of financial products within native networks’ currency.
Key challenges
Collaboration between financial institutions is a challenge, as all are players in a competitive landscape.
At the same time, financial institutions understand that in order to bring innovation to traditional money transfer systems, they must work together with digital companies to speed up technology integration in the financial industry and sort out a formidable layer of regulatory complexity.
What do we have today?
The current systems and workflows for money transfers between financial institutions are too complex, requiring multiple steps to reduce risks and frauds. A similar process is used for all kinds of transactions: both for settlement of regular retail payments, and huge institutional transfers. These limitations affect many institutions.
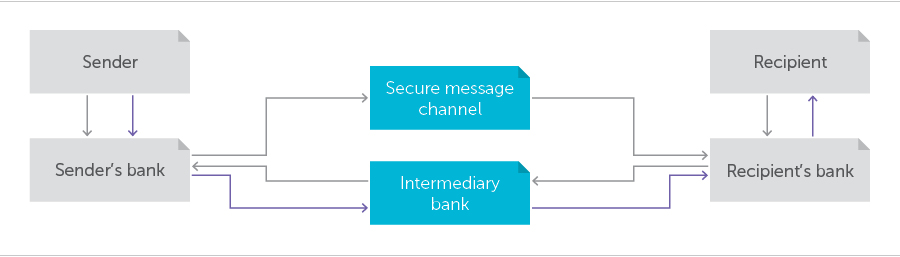
In the picture below, the classic money transaction workflow is represented. The gray channel represents transfer request and authorization data, the green channel represents money flow. The system works through the following steps:
- The consumer (Sender) creates a request for the financial instituti on to transfer an amount of money to a specific recipient [to identify the recipient, the sender uses International Bank Account Number (IBAN) or Bank Identifier Code (BIC)].
- The sender’s bank sends the message through a secure message channel to the recipient's bank with the same request to transfer the specified amount.
- The last step: the recipient's bank responds to the sender’s bank’s message/request for money via Intermediary Bank.
Adapting business models to decentralized payment
The decentralized system uses a common selection of protocols to process tasks across many separate stakeholders’ nodes rather than through one central point. But this approach requires user confidence in a central counterparty.
The decentralized payment model allows consumers to transfer money, which is typically covered by additional secured processes like blockchain technology with smart contracts or a set of cryptographic actions.
For example, “cryptocurrency” uses a single distributed ledger and assigns payments between customers in a native “currency.” The best implementation case of this distributed payment protocol is the Bitcoin network, which owns its own native currency—Bitcoins.
At the same time, many companies (mostly startups) have launched competing decentralized schemas, with different/unique encryption technology or focusing on different use cases.
Recently, two large banks, Goldman Sachs and Barclays, jointly started working on an alternative cryptocurrency controlled by traditional banks. Financial institutions are deciding, one by one, to invest in the growth of alternative payment networks as an extension to existing networks.
But it’s not exactly the exchange that was discussed by analysts couple years ago—financial institutions are starting as a narrow entrance into these networks, launching financial products that are connected to non-traditional or alternative payment platforms.
Within SoftServe’s BFSI labs, we run multiple researc h and development projects based on this decentralized approach – DLT (distributed ledger technology) systems and inscription protocols for data transfer. The key, identified benefits include:
- Cryptographic protocols dramatically improve security;
- Transaction time in near-real time;
- Transaction cost is multiple times lower; and
- Transparency and traceability of transactions are similar to classic systems, when end-user identification may be an issue.
To learn more about our BFSI capabilities, check out our BFSI team, or contact us directly today.

