
Don't want to miss a thing?
Serverless Architecture: Building Smarter Chatbots
Chatbots and voice assistants are being applied across a wide range of industries, from customer service to healthcare and finance. This transformation is driven by cloud-native AI services, which provide the intelligence behind conversational interfaces, enabling applications to listen, talk, and understand users.
At the same time, serverless architecture provides a scalable and cost-efficient foundation for running these solutions. By using managed services that scale automatically, developers can focus on chatbot functionality without worrying about infrastructure management.
Cloud-native Services Powering Chatbots
Cloud-native services provide the foundation for quickly building applications that assist users with everyday tasks using natural language processing (NLP). With these tools, personal assistants can:
- Search and aggregate information from multiple data sources, giving users quick access to the information they need.
- Automate routine tasks, such as scheduling meetings, sending reminders, or managing emails.
- Perform actions on behalf of users, including making bookings, placing orders, or updating records.
Exploring Different Types of Chatbots
Chatbots can serve a variety of purposes depending on their design and the needs of the users. The main types include:
- Informational Bots
These bots provide users with data on request. Examples include delivering the latest weather and news updates, sports scores, calendar information, geo-location data, social media notifications, and email summaries. Informational bots help users quickly access relevant information without switching between multiple apps or services. - Application Bots
Application bots act as interfaces to mobile applications, such as Siri, Google Assistant, Alexa, or Cortana. They streamline routine actions, including booking tickets, managing calendars, placing orders, or calling taxis. By providing a conversational interface, these bots make interactions with apps faster and more intuitive. - Enterprise Productivity Bots
These bots are designed to improve communication and workflows within businesses. They can enhance customer experiences, automate internal processes, boost operational efficiency, and reduce the cost of customer service. For example, enterprise productivity bots can monitor stock trends, notify users of important changes, and execute repetitive tasks automatically or semi-automatically. - IoT Bots
IoT (Internet of Things) bots provide conversational interfaces for connected devices such as smart watches, smart speakers, and home automation hubs. They allow users to control devices, retrieve information, and manage their environment through natural language commands.
Cloud Services for Conversational Interfaces
Major cloud providers like Amazon and Google offer specialized services for building conversational interfaces using both voice and text. Amazon Lex and Google Dialogflow are prime examples. These platforms provide developers with pre-built tools, standard integrations, and common usage patterns that simplify the creation of chatbots and voice assistants.
While these cloud-native services offer many advantages, such as rapid development and managed infrastructure, they can have limitations when it comes to building highly flexible or fully customized solutions. Businesses with unique requirements may need capabilities beyond what standard integrations provide.
To address these challenges, SoftServe’s Centre of Excellence (CoE) Solutions team set out with specific technical goals to develop a flexible enterprise-grade chatbot solution:
- Develop and validate a serverless architecture for chatbots on the AWS Cloud platform.
- Enable custom integration with any messaging platform, not limited to the predefined integrations offered by cloud providers.
- Integrate with interactive web applications using WebSocket technology to support real-time communication.
- Ensure secure authentication to corporate networks without exposing user credentials.
Big Picture: How Serverless Chatbots Work
To achieve the CoE team’s goal of building a flexible, serverless chatbot architecture, conversation design services such as Amazon Lex and Google Dialogflow play a central role. These platforms provide integration with voice assistants and messaging clients, along with natural language understanding (NLU) functionality, allowing chatbots to recognize user intent and retrieve data from external APIs to fulfill requests.
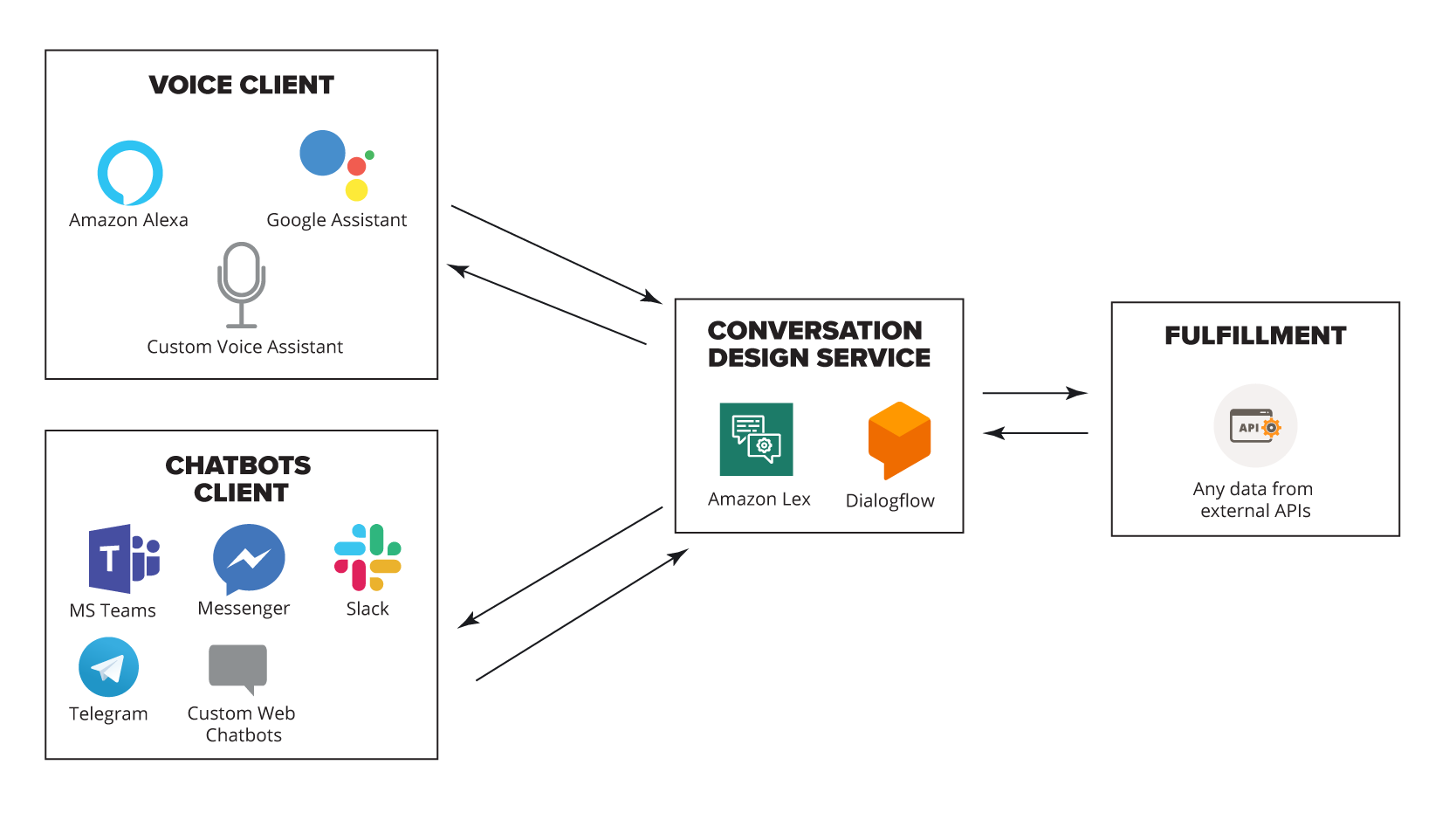
These conversational interfaces leverage advanced deep learning for automatic speech recognition and natural language processing. A key feature is multi-turn conversations, which manage the user’s session context and orchestrate dialogue steps to collect all information before executing a user request.
Integration with AWS Lambda and a serverless architecture adds another benefit: developers can build fully managed, event-driven solutions without upfront infrastructure costs. This aligns perfectly with the CoE team’s objective to create a flexible, scalable architecture for enterprise chatbots.
By default, Amazon Lex supports popular chat services such as Facebook Messenger, Slack, and Twilio SMS. For other messaging platforms not predefined by Lex such as Telegram or Microsoft Teams a custom integration solution is required.
Custom Chat Messenger Integration
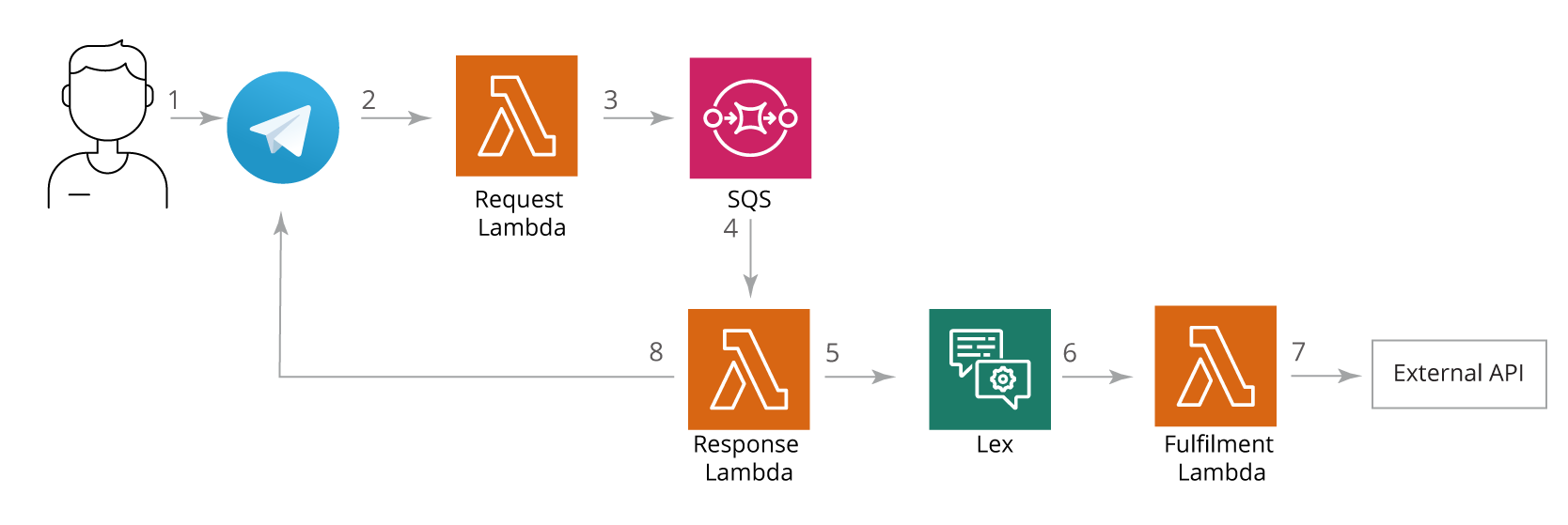
When a user interacts with a chatbot via a text messenger, the request goes through several steps to ensure proper processing and fulfillment. For example, if a user asks: “Book a hotel room for a week starting from September 1.”
The workflow proceeds as follows:
- Request validation and authentication
The Request Lambda function validates the user’s request and authenticates the chatbot to ensure secure processing. - Task queuing
The Request Lambda then sends the task to a queue and provides an immediate response to the client to prevent retries from the messenger. - Processing the request
A Response Lambda is triggered by the task in the queue. It sends the user’s message to the Amazon Lex service. - Understanding and decision-making
Based on the message context, the Lex bot processes the text input and determines which business logic should be executed to provide the correct response. - Triggering external actions
If needed, a Fulfillment Lambda can call external services or APIs, such as a hotel booking system. - Sending the response
The Response Lambda sends an asynchronous response back to the chat client.
The Lex bot maintains conversational context and can ask clarifying questions if additional information is needed. For example:
- User: “Book a hotel room for a week starting from September 1.”
- Lex bot: “In which city would you like to book a room?”
- User: “London.”
With this additional context, the Lex bot completes the booking.
Integrating Chatbots With Web Applications
To enable chatbot functionality within a web application, the team used WebSocket APIs via Amazon API Gateway. WebSocket APIs allow developers to build real-time chat applications while following an event-driven, serverless approach.
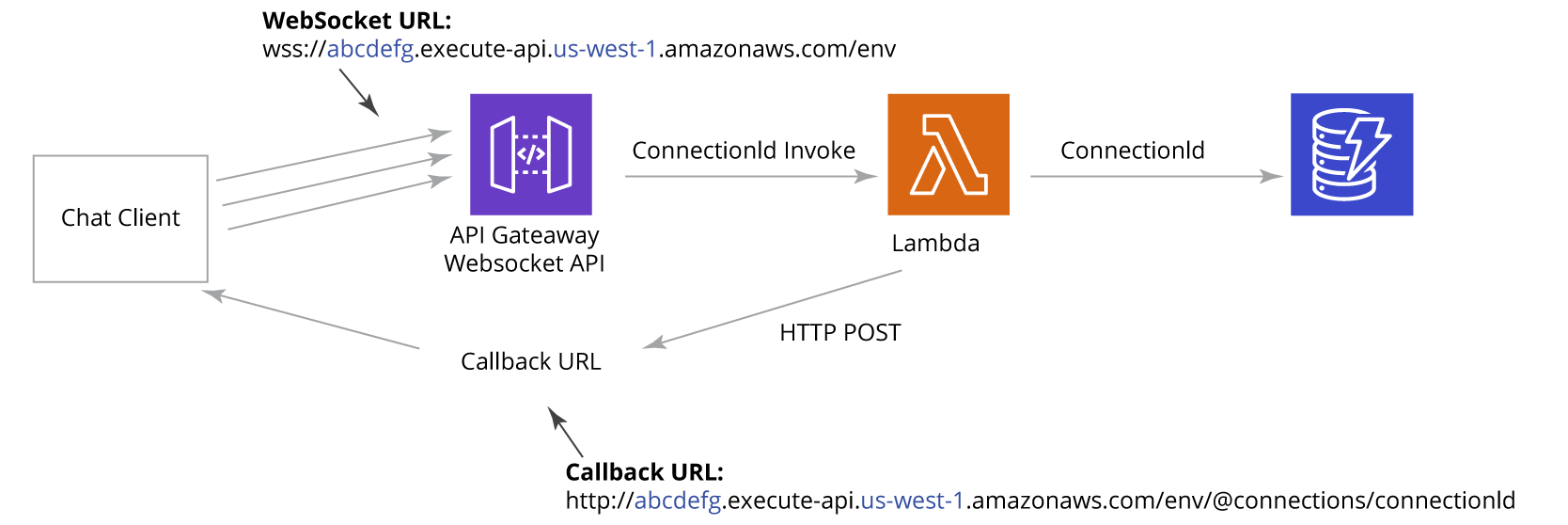
Key components of this setup include:
- Web chat clients connect to the WebSocket URL to send requests.
- The WebSocket API manages server-client connectivity.
- A Lambda function is triggered for each message, containing the client’s connection identifier.
- DynamoDB tracks connection identifiers to manage all active sessions.
- The chat client listens to a callback URL to receive responses in real-time.
The final solution reuses the architecture developed for messenger integration while adding web-specific infrastructure. This allows real-time communication, scalability, and all the benefits of a serverless, cloud-native design.
With messaging and web integrations working seamlessly, the next priority is secure authentication so the chatbot can safely interact with third-party services and corporate resources.
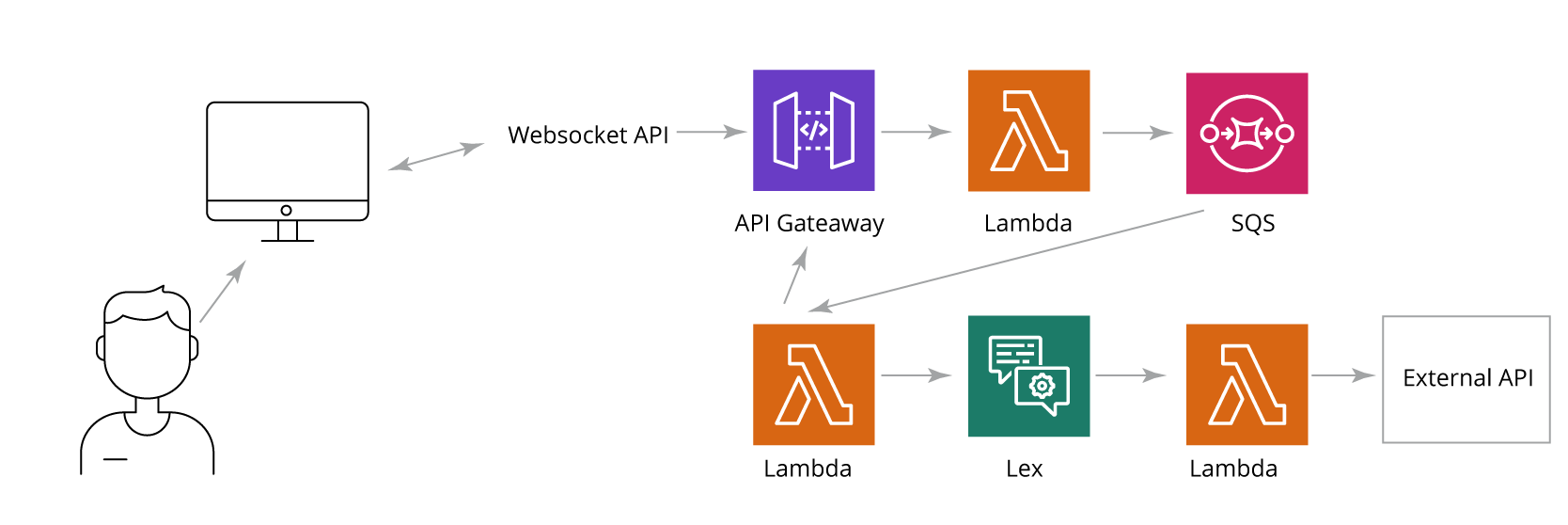
Secure User Authentication for Chatbots
When a chatbot performs tasks on behalf of a user such as accessing booking systems or corporate resources, authorization is required. Sensitive credentials cannot be entered directly into a chat or web form, so the team implemented the OAuth2 authorization flow.
Amazon Cognito was chosen to manage access, offering:
- Native access control for API Gateway and Lambda functions
- Sign-in via social identity providers (Google, Facebook)
- Integration with enterprise identity providers (Microsoft Active Directory via SAML)
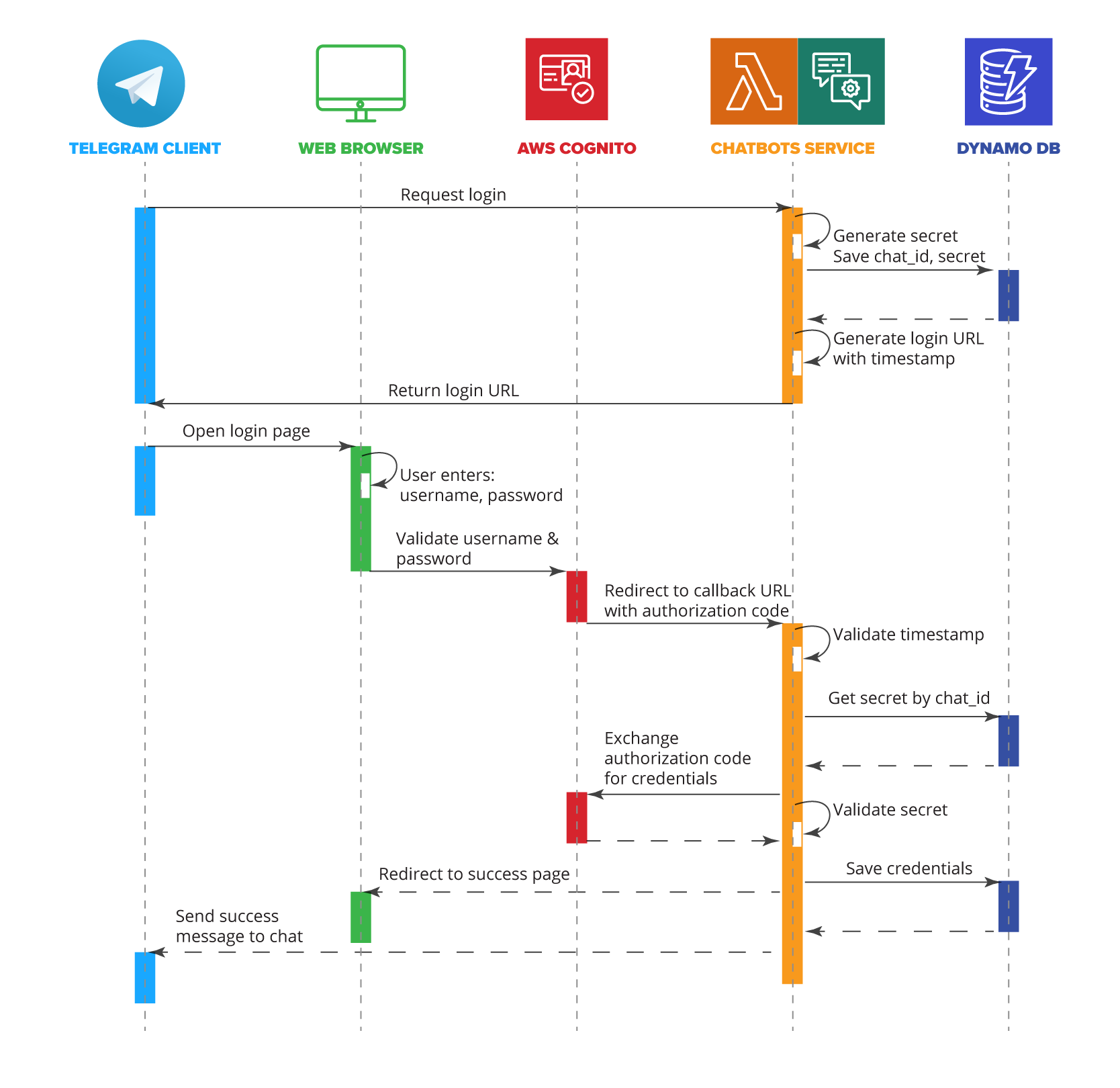
Authorization steps:
- The chat client sends a login request.
- The service generates a secret key, stores it in DynamoDB, and returns a login URL with a timestamp.
- The user enters credentials into the Amazon Cognito web form.
- The OAuth2 code grant type exchanges the authorization code for an access token.
- Cognito validates credentials and redirects the user with an authorization code.
- The chatbot service verifies the secret, exchanges the code for credentials, and stores them in DynamoDB.
- The user is redirected to a success page, and the chat client receives confirmation.
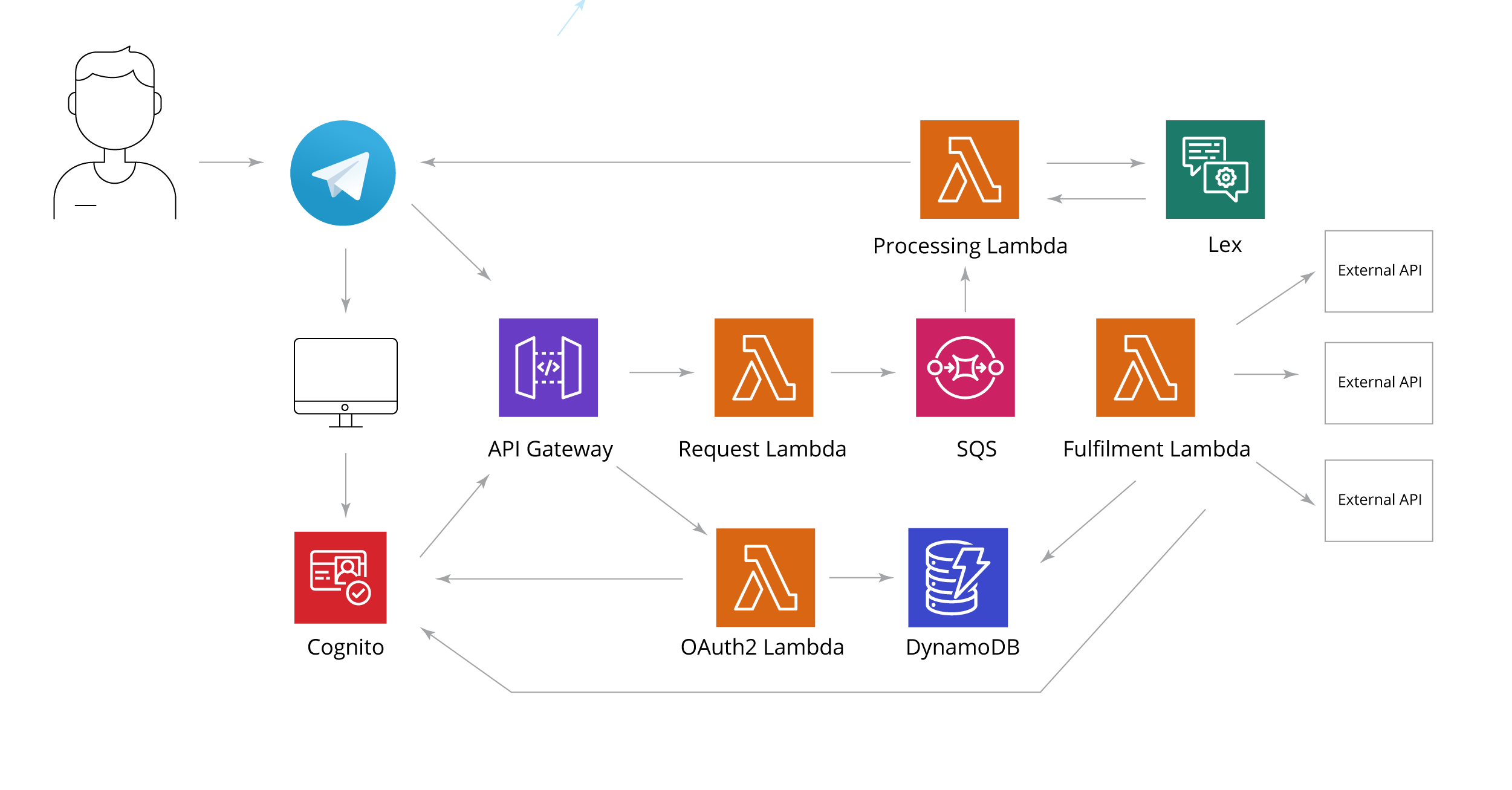
The Complete Serverless Chatbot Solution
The final serverless, cloud-native solution on AWS combines all components:
- Integration with any chat messenger
- Real-time web applications
- Secure OAuth2 authorization
- Support for third-party identity providers
- Fully managed, horizontally scalable cloud services
This architecture demonstrates how serverless design can simplify development, reduce infrastructure overhead, and provide enterprise-grade flexibility.
Summary and Next Steps
SoftServe’s research shows that chatbots and voice assistants are now mature technologies. Cloud providers offer powerful tools to build conversational interfaces that closely resemble natural human interaction, reducing friction and errors.
The flexible, serverless architecture designed by the CoE team supports custom chat clients, third-party identity providers, and complex business logic, while meeting enterprise needs such as scalability and high availability.
Next steps: creating a SoftServe internal chatbot to automate business trip booking and reporting.
If you have innovative ideas, let’s build the future of chatbots together.
Start a conversation with us
