
Don't want to miss a thing?
Successfully Develop SaaS Storage Strategies with AWS
COMMON SAAS PATTERNS ON AWS
The most commonly used SaaS patterns on AWS include silo, bridge, and pool partitioning models. Each partitioning model comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
SAAS STORAGE PARTITIONING MODELS
Each modern partitioning model features distinct approaches to management, data access, and tenant data separation, as shown here.
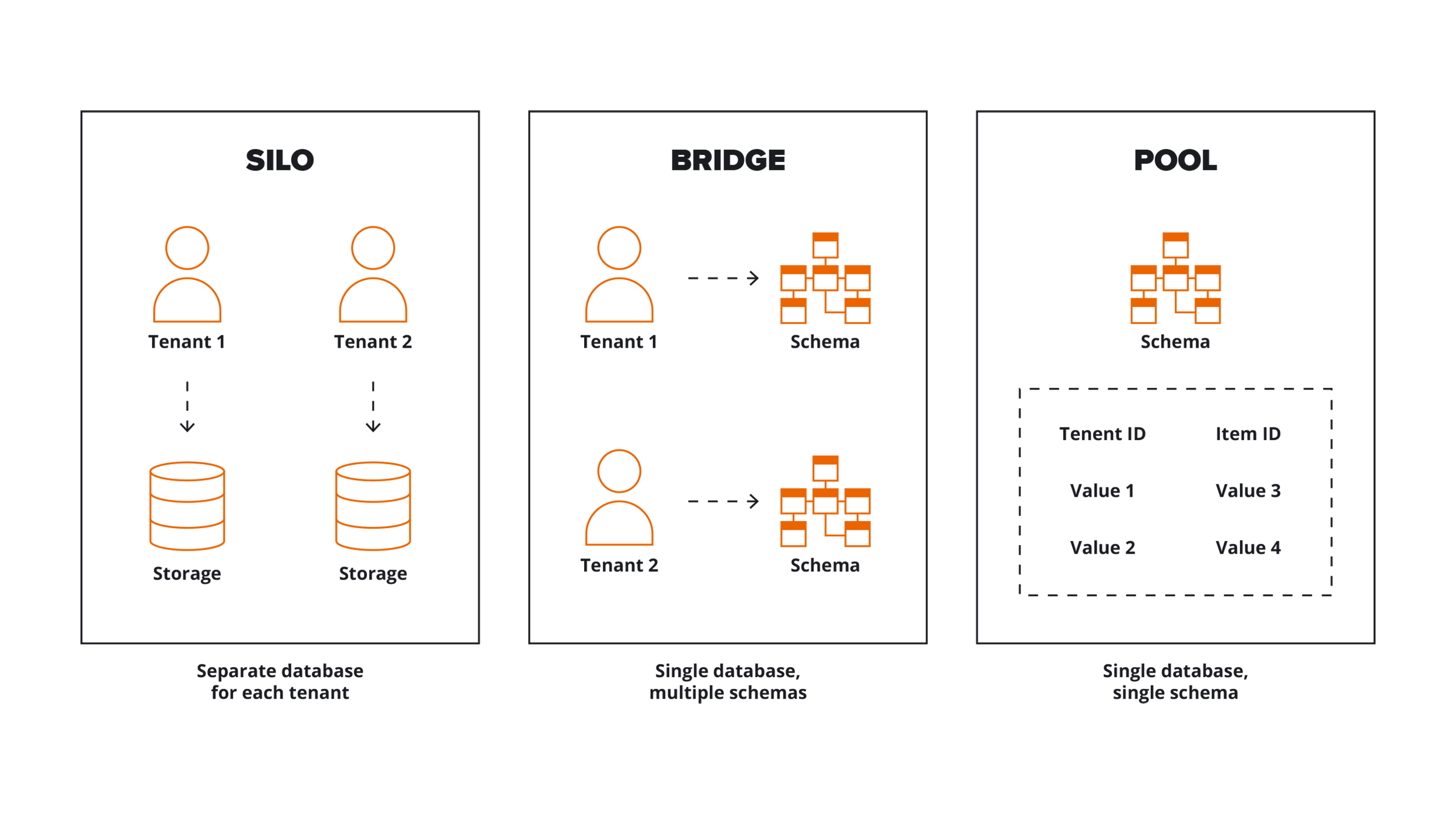
Silo model
In a silo storage model, developers entirely isolate tenant data from other tenant data.
All components of each tenant are unique to the client, meaning each tenant has separate representation, monitoring, management, and security.
Bridge model
A bridge model is most often considered a compromise-type model for SaaS. While the model still offers separation of the tenants, a single database stores all data. Division in a single database is achievable by creating different tables with different tenants, managing the access rights to the tables with data representation.
Pool model
A pooled model enables tenants to share all resources. Since one database stores all data, all tenants can share a schema. The pool model approach has additional requirements for access control to the tenant data. To simplify provisioning, management, and updates of the SaaS solution, use pooled models. Agility and continuous delivery become increasingly achievable.
AREAS OF CONSIDERATION
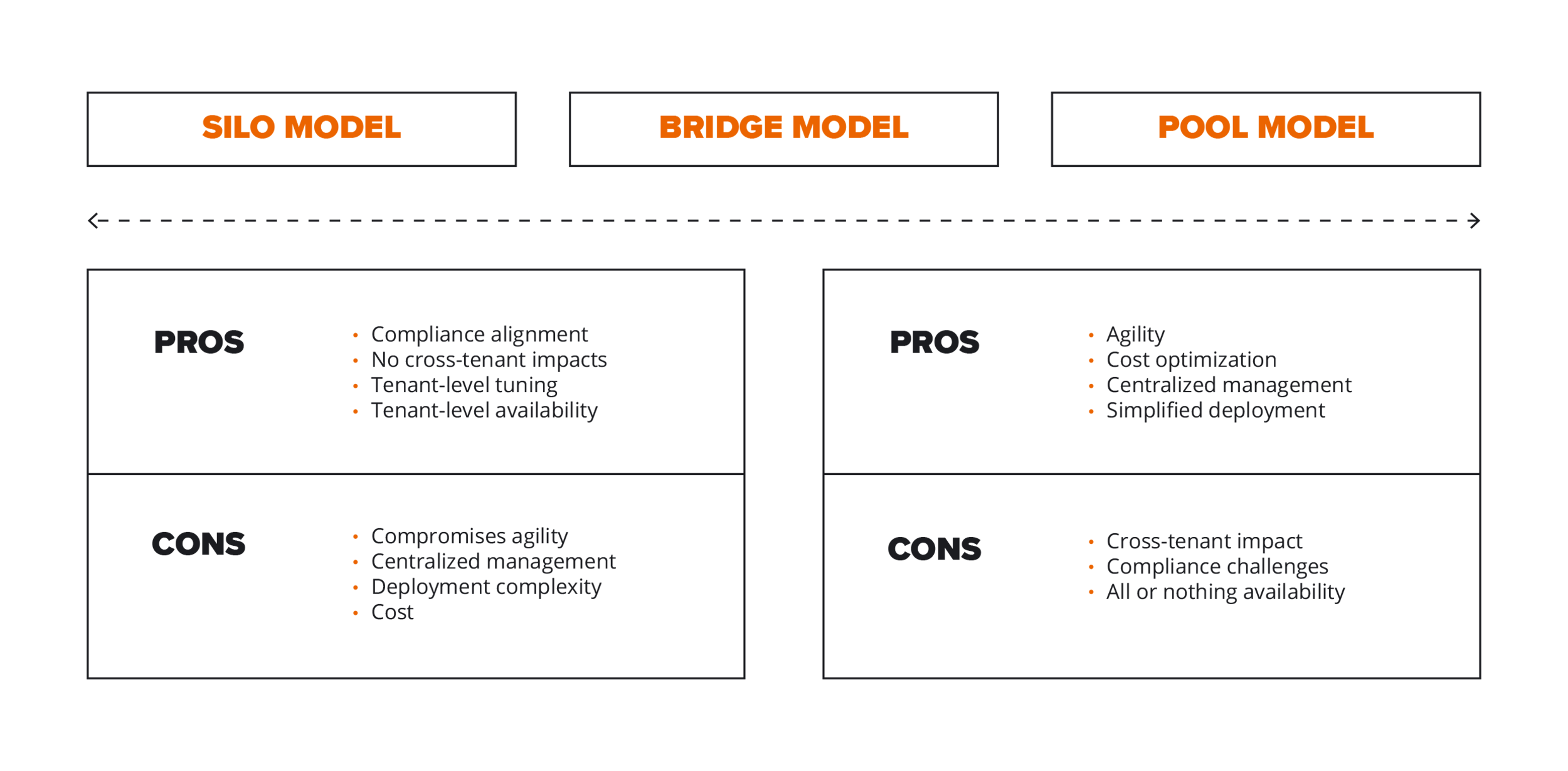
While each model has its pros and cons, the best choice is not always immediately clear when aiming to fully align with tenant isolation requirements. Partnering with a trusted expert can often provide a clearer path to a successful implementation.
When selecting a storage model, architects must consider a variety of factors. The silo model is often preferred for migrations from existing infrastructure, as it allows for an easier transition without requiring changes to the SaaS application code. On the other hand, the pool model is widely regarded as efficient and agile, particularly when building an environment designed for rapid and continuous releases.
Ultimately, the primary goal should be to understand the combination of business and technical factors that drive the selection of the most suitable strategy.
CONCLUSION
The storage needs of SaaS architecture can be complex and challenging. Users must carefully evaluate which combinations of SaaS multi-tenancy storage options best align with their business requirements, customer needs, and other critical factors.
Since no single solution fits every company, a variety of options are available to meet the unique needs of individual organizations. While some models align well with basic concepts, others are more complex, and certain AWS storage technologies are better suited to support multi-tenancy. For instance, building a siloed model on Amazon Relational Database Services (RDS) is often considered less sophisticated than using DynamoDB.
Users must thoughtfully assess how their multi-tenant application architecture and diverse requirements integrate with AWS storage technologies. Additionally, it’s essential to consider how tenants will access the data. AWS offers a wide range of storage services designed to address any SaaS multi-tenant storage challenges.
For further information or assistance with your AWS needs, contact SoftServe today—an AWS APN partner.
Start a conversation with us
