
Don't want to miss a thing?
DLT 2.0: It’s All About Scalability
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) transforms how businesses conduct transactions, create contracts, and manage operations. But scalability is still a big challenge for most DLT systems because many were developed without a clear long-term vision.
Take Bitcoin as an example — a cryptocurrency built on blockchain, a form of DLT. While Bitcoin is incredibly popular, it wasn’t designed to scale effectively. As more people use it, transaction speeds have slowed drastically. For comparison, Visa can process 24,000 transactions per second, while Bitcoin manages only around five.
DLT’s structure is unpredictable. Built block by block, it’s hard to predict how the system will evolve. However, scalable DLT solutions are possible.
This article looks at how agent-based modeling (ABM) serves as a predictive tool to address scalability issues in DLT solutions.

APPLICATIONS FOR DLT
DLT is used in many industries. It secures identities, protects sensitive data, enables real-time payments, and improves interoperability between banking systems. One of the biggest benefits of DLT is immutable storage — once data is recorded, it can’t be changed or tampered with. This ensures transparency and builds trust among users.
DLT makes it possible to create new distributed features while cutting out the middleman. It also makes it easy to use cryptocurrencies or tokens for payments within the DLT ecosystem. This streamlines transactions and automatically takes care of maintenance costs.
Despite the advantages, scalability is still a challenge. As the network grows, can the infrastructure handle the increasing demand?
If you want your business to thrive long-term, it’s important to start with the big picture and work backwards. If you focus too much on individual transactions or network participants, you'll overlook how the solutions will evolve. Without proper planning, the network could eventually collapse.
HOW ABM HELPS DLT GROW
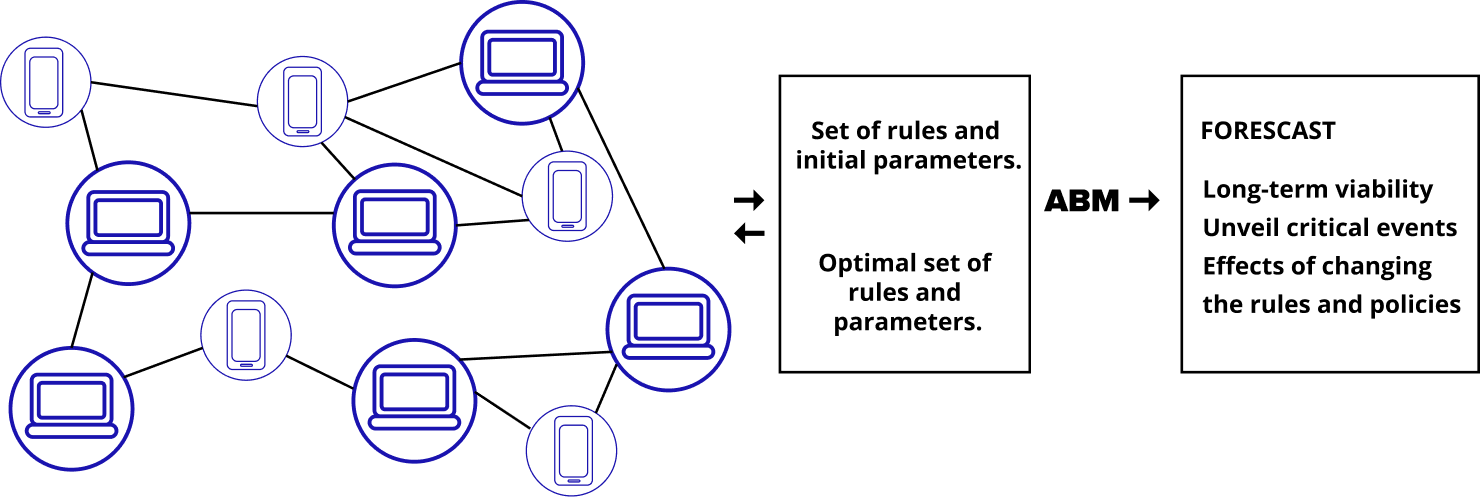
Agent-based modeling (ABM) is a powerful way to simulate complex systems. While it has been around for decades, its use in DLT is relatively new.
ABM works by reverse engineering to simulate how agents — autonomous entities that make their own decisions — interact within a system. These agents represent different participants, like households, institutional investors, or individual customers. Each agent follows a set of rules that guide their behavior and interactions with others.
ABM stands out because it captures complex, dynamic behaviors that traditional models miss. It links the behavior of individual agents to give results that are comprehensive and dynamic, not linear and static. This flexibility helps ABM handle unexpected events and patterns, known as emergent phenomena, found in many scientific fields. As a result, more businesses now use ABM to solve complex problems.
Applying ABM to test scalability in DLT is a natural fit. ABM analyzes large, dynamic patterns of how components interact, creating simulations that reflect real-world outcomes.
With ABM’s ability to model large-scale interactions, businesses can:
- Make more accurate predictions about system behavior
- Clearly define the actions of individual agents, potential transactions, and strategies as nodes on the blockchain
- Ensure natural scalability by managing discrete actions at each step
Simulating a business network and its transactions on a larger scale is a smart way to see how stable and efficient the system will be over time. It’s a chance to spot issues early and avoid the unexpected failures or disruptions that often happen with DLT solutions when long-term growth isn’t fully considered.
ABM simulations have two key facets:
- Discrete event simulations model individual transactions in the DLT step by step
- Object-oriented programming treats each participant on the network as an “object” with its own properties and methods for interacting with the environment
WHY ISN’T ABM WIDELY USED IN DLT?
Given the powerful capabilities of ABM, why isn’t it always used in DLT structures?
One big challenge is the complexity of combining ABM with DLT systems. It requires specialized expertise in advanced fields like statistical physics and bioinformatics, which is hard to find. This knowledge is needed to understand the intricacies of DLT and make it scalable with ABM.
At SoftServe, our team includes PhD-level experts who are leaders in their fields and have strong ties to top academic institutions. This knowledge helps us deliver effective ABM-driven DLT solutions that meet our clients’ needs.
Even with the right expertise, financial services managers need to be cautious. They should set clear expectations and do proper due diligence when they develop DLT solutions. The unique nature of DLT — its platforms, technologies, and evolving structure — requires extra attention to ensure everyone is working toward the same goals.
DLT solutions often fail because they lack a clear, long-term vision. That’s why ABM is so critical: without a fixed direction, systems are prone to instability. To minimize financial and functional risks, you should test and validate from the start, rather than make assumptions in strategy, design, and planning.
DLT IN ACTION: CASE STUDIES
Commodity trading
Commodity trading relies on managing letters of credit between counterparties, a process that is expensive and time-consuming. SoftServe worked with a client to show how DLT simplifies and scales this process as the commodity exchange grows.
The client used blockchain to address information asymmetry and the high transaction costs — both major causes of trade finance gaps. The DLT-based platform provided an alternative to traditional letters of credit in commodity financing. By removing the need for these letters, the solution reduces transaction costs to a small commission and cuts down on the time required to manage the process.
DLT also increases access, especially for smaller businesses. Banks often prioritize high-volume borrowers due to regulatory demands, which makes it harder for smaller importers and exporters to secure financing through traditional channels. DLT bridges this gap, allowing businesses of all sizes to join the ecosystem.
Trades happen faster with DLT, and in commodity trading, timing is everything — especially when delivery deadlines are tight. Traditional letters of credit take time to process, sometimes delaying deals to the point where they fall apart. DLT speeds up transaction time.
Scaling a financial ecosystem helps everyone, from big enterprises to institutional investors. Yet scalability needs to be stable and predictable. To ensure this, SoftServe applied ABM to assess transaction loads and ensure the scalability of the financial ecosystem.
Adjoint
ABM-based DLT also has broad applications across financial services, from transactions and loans to insurance. A working model helps you understand every part of a proposed system. It gives you valuable insights into how the system could work, helps you identify the best rules and transactions, and shows how it might handle challenging situations or unexpected events.
SoftServe partnered with Adjoint to use smart contracts, making financial transactions faster, more secure, and more private. Adjoint’s Uplink is an open-source platform that lets businesses easily deploy, maintain, verify, and execute smart contracts on a private, permission-based ledger. SoftServe helps clients adopt and integrate the Uplink platform.
SCALE FOR THE FUTURE
For DLT to work effectively, it needs to scale. ABM ensures that. By running complex simulations, ABM-powered DLT predicts scenarios and adds value to the ledger. It minimizes surprises and ensures long-term success. Unlike traditional models, ABM captures chaotic, nonlinear behaviors on an individual level. This lets you model real-world complexity with accuracy.
This level of predictability is a game-changer for businesses adopting DLT. With ABM, companies can move forward with confidence, knowing their systems are built to adapt and scale.
Wondering how your DLT solution will grow with your business? Contact SoftServe for a free consultation.
Start a conversation with us
