
Don't want to miss a thing?
The New Era of ESG and Why It’s Essential for Business Success
The term sustainability was first coined to describe the impact of human activities on the surrounding world. Initially used by scientists and governmental organizations in Europe, the term gradually evolved to encompass specific parameters, results, and dependencies as conversations around the topic progressed.
Many new stakeholders — especially businesses — began joining the conversation. Then, the more business-oriented term ESG (environmental, social, and governance) appeared, encompassing business risks, company stakeholders, and investing frameworks. Sustainability is part of ESG, but it isn’t the complete definition or explanation. ESG is a different term addressing the same subject with a more defined scope. Today, ESG and sustainability are used interchangeably.
Here’s a breakdown of major ESG issues and their societal impact.
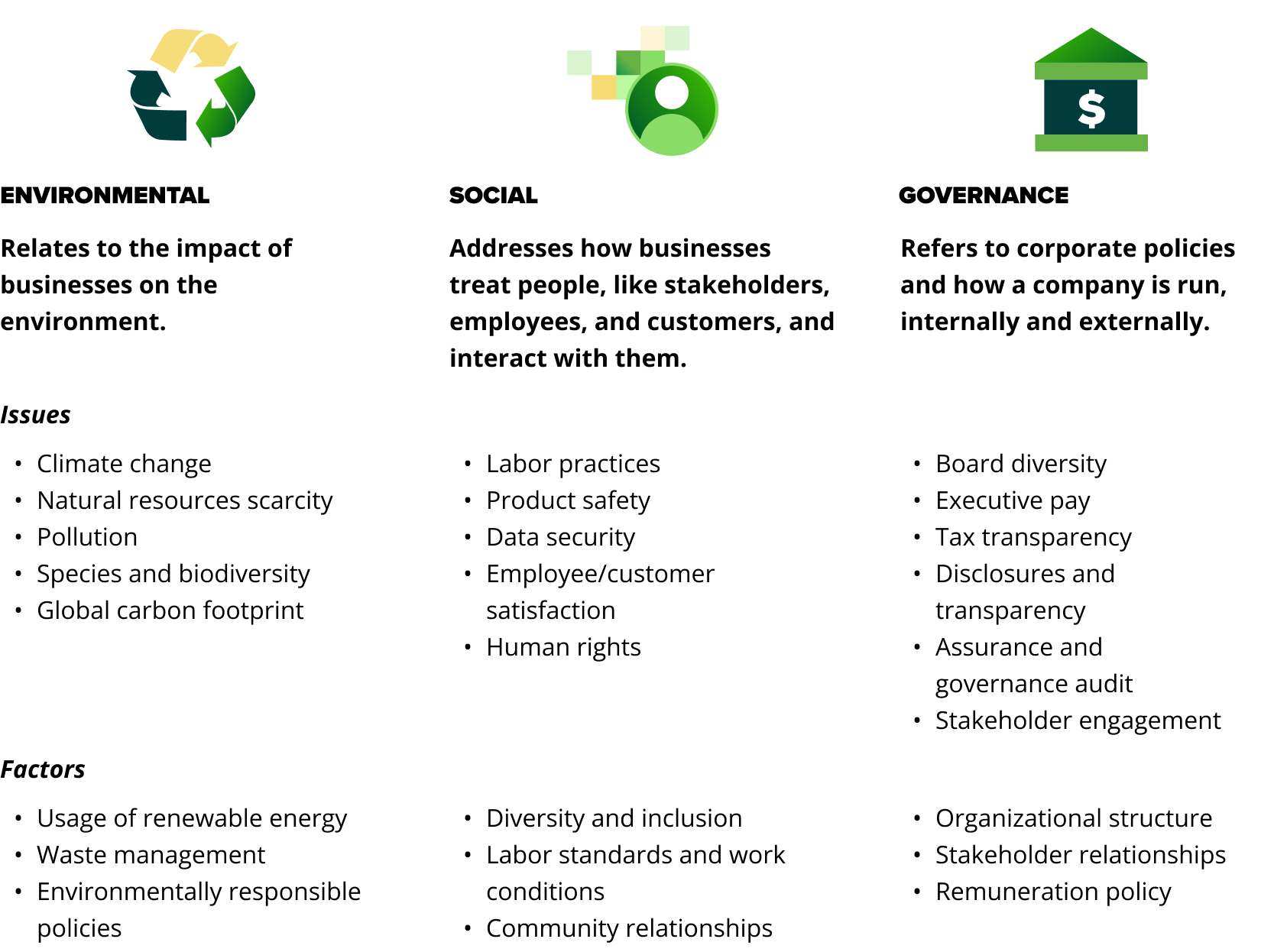


ESG and sustainability drivers and challenges
For over 15 years, many activists, authorities, countries, and business leaders have discussed and creatively considered ways to address global ESG and sustainability topics.
The topic became so urgent that:
| Financial institutions | Investors | Customers and consumers |
| are incorporating ESG and sustainability parameters into their risk management services, along with the calculation of ESG scores. | are making investment and portfolio management decisions based on ESG ratings, providing a holistic assessment of a company’s long-term risks. | have shifted their attitudes and behaviors toward sustainability. They are considering both the producer’s and the product’s footprints of ESG and sustainability initiatives, from environmental friendliness to social responsibility and economic inclusiveness. |
Read Deloitte's latest article on how consumers are embracing sustainability for more insight into this trend.
In addition, ESG and sustainability frameworks, principles, and guidance have emerged, resulting in a competitive landscape for businesses to develop regulatory and industry compliance guidelines.
Companies looking to secure capital are focused on meeting ESG metrics, often relying on vendor vetting and partnerships guided by ESG scoring. ESG scoring impacts the overall value chain and underlying supply chains, and — as public opinion grows in power — leads to major financial impacts on the company, pushing them to uphold these standards as a responsible employer and business.
ESG BENEFITS
LOWER COST OF CAPITAL
- Companies with higher ESG scores typically enjoy a reduction of around 11% in their loan capital costs.
- The financial impact of poor ESG performance is evident: Over a five-year period, ESG controversies and low ESG scores caused a loss of more than $530 billion in value for 24 large U.S. companies.


IMPROVED INVESTOR RELATIONSHIPS
- The vast majority (84%) of investors report that they actively consider ESG ratings when selecting investments.
- Integrating ESG ratings into portfolio management models is already widespread among institutional investors, with 92% reporting that they do so.
ESG CHALLENGES
LACK OF DIGITAL EXPERIENCE, DATA MATURITY, AND QUALITY
- Companies face the challenge of embracing digitalization to effectively address ESG concerns.
- Companies must establish ongoing, real-time internal data collection, organization, and integration processes.
- Many companies lack the necessary infrastructure to handle full-scale data integration.

DEPENDENCE ON THE VALUE CHAIN AND SUPPLIER ADVANCEMENT
- To embrace ESG principles, companies must restructure their relationships with suppliers and vendors, who often fall behind in this area.
- Given the complexities of managing AI/ML models, many vendors and suppliers lack the internal expertise to handle multiple machine learning models.
ESG CHALLENGES
HARD TO SELL BUSINESS CASES
- Achieving effective ESG management policies requires a complete understanding of the ESG indicators throughout the value chain.
- Low ESG ratings could result in companies being excluded from the value chain.


DISPARATE METHODOLOGIES AND ESG RATINGS
- More than half (56%) of retail customers report that ESG scores influence their purchasing decisions.
- An overwhelming majority (91%) of students express a desire to work for an ethical company.
A new era for ESG and sustainability
Over the past few years, businesses have increasingly embraced ESG and sustainability as a trend, with nearly every company including ESG and sustainability goals on their agenda. As this trend continues, companies are publicly communicating their ESG commitments and progress. Investors’ perceptions of overall business effectiveness on priority outcomes were partly shaped by corporate reporting, one of many sources of information they use to assess a company’s activities and performance. Regrettably, investors often do not trust these reports because companies frequently discuss sustainability topics vaguely without providing accurate descriptions and sufficient data.
In PwC’s Global Investor Survey 2022, a majority of the investors surveyed think corporate reporting contains unsupported sustainability claims (i.e., greenwashing).
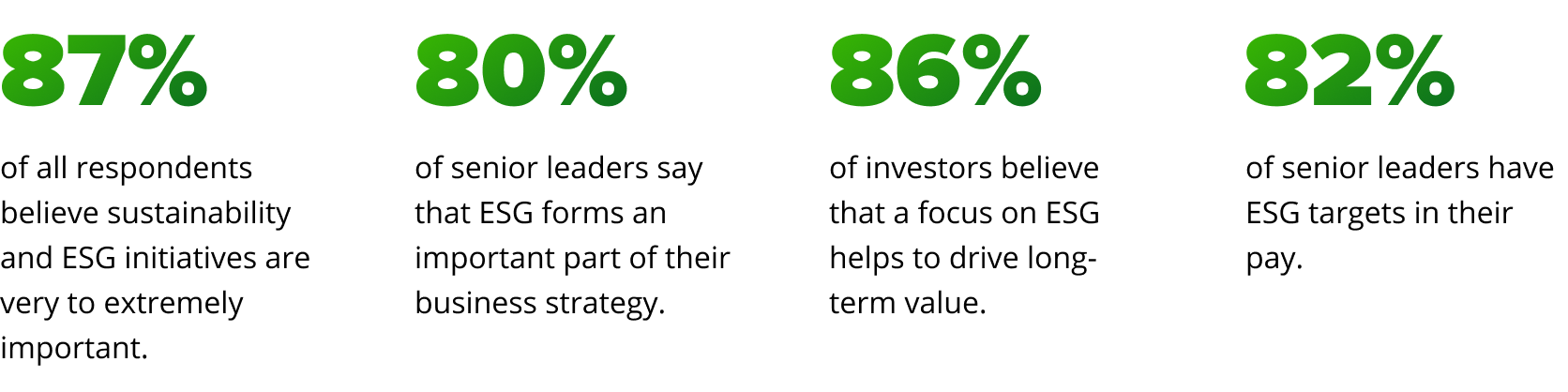
Sources: PwC's Paying for good for all report 2022 and Ernst & Young C-suite Insights: Sustainability and ESG Trends Index.
The data from these industry reports proves that ESG and sustainability remain relevant, require more transparent reporting, and are high-priority initiatives on executive agendas.

according to Ernst & Young LLP in their most recent C-suite Insights: Sustainability and ESG Trends Index.
We are entering a new era of ESG, where voluntary initiatives are becoming mandatory. Over the next few years, the topic will be clearly defined, and the regulatory landscape will provide specified requirements and authorities to report to. Meanwhile, companies are still determining what ESG means, establishing targets, tracking progress, and creating new programs to generate positive impacts.
PART 1: ENTERPRISE ESG & SUSTAINABILITY LANDSCAPE
When it comes to the ESG landscape, it is critical to acknowledge the significance of diversifying business initiatives from an environmental, social, and governance perspective. It is also important to connect these efforts to the impact that companies have on the environment and the people within it.
The figure below illustrates the ESG and sustainability landscape every organization must integrate into their business and digital strategies as part of their long-term strategic planning.
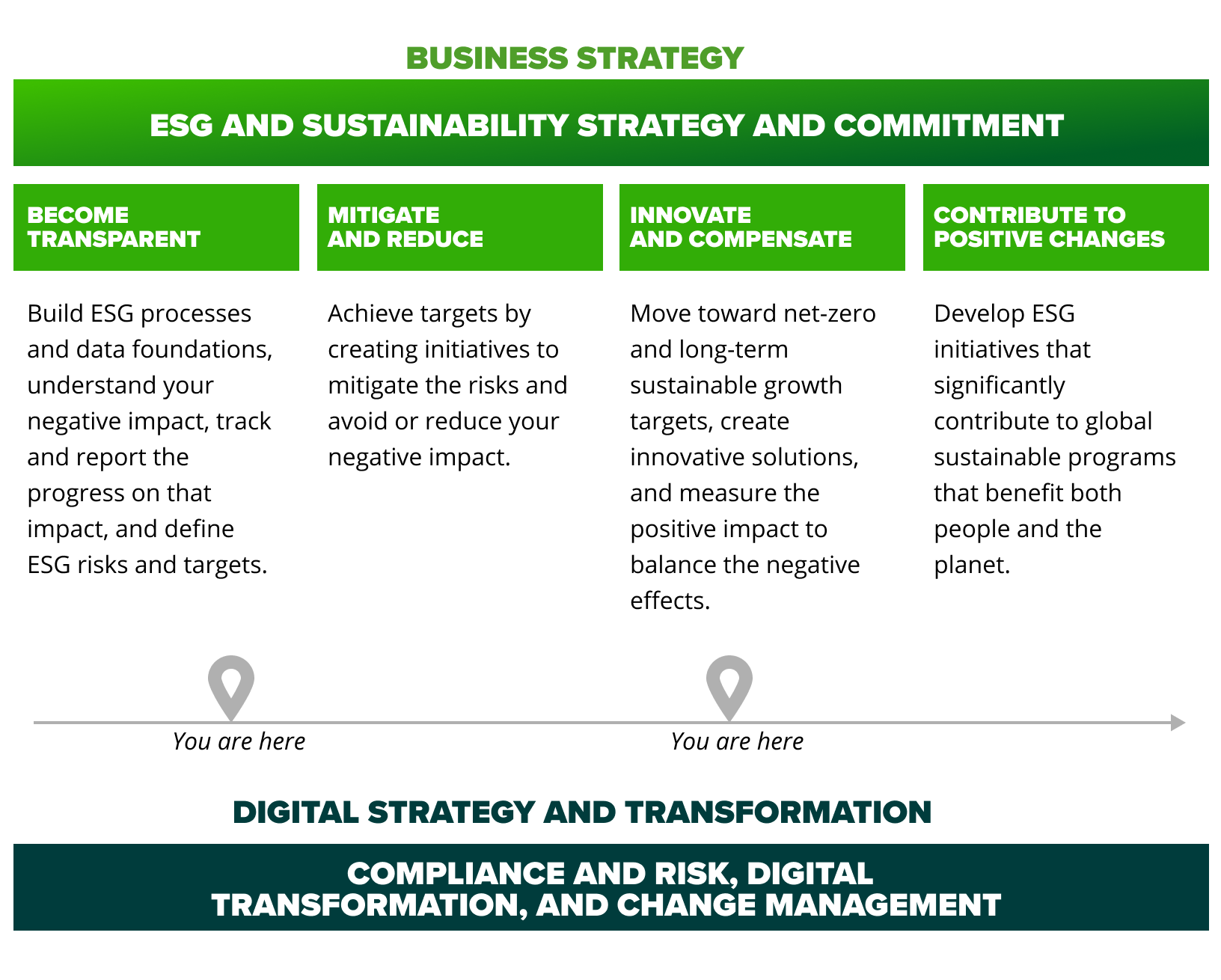
ESG and sustainability strategy and commitment
Well-known consulting firms have already established themselves as ESG advisors, helping clients define their ESG and sustainability strategy, required governance, and target operating model (TOM). This is done to ensure ESG integration into the business strategy at every level of the enterprise, balancing aspects related to the planet, people, and profit.
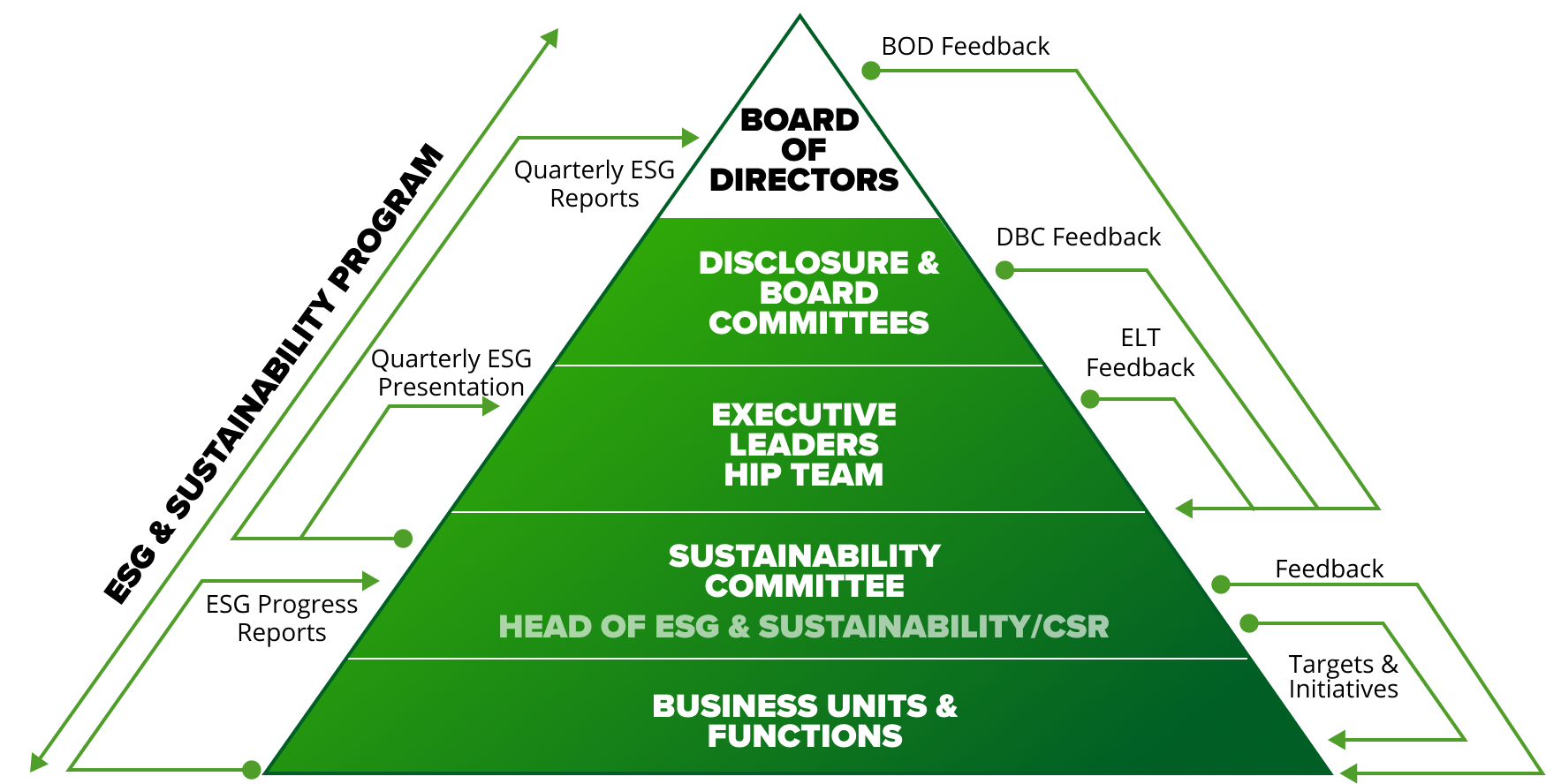
If properly set up, the organization
will understand its:
ESG risks impacting the company
ESG trajectory for the business to:
- Contribute to some of the sustainable development goals (SDGs)
- Comply with worldwide sustainability standards, policies, and frameworks, like The United Nations Paris Agreement, GHG Protocol, and Global Reporting Initiative (GRI)
- Comply with the commitments of the countries where business operations are conducted
- Comply with the industry ESG regulations, requirements, and policies the business operates in
ESG commitments, in the perfect scenario, are defined in a SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound) way. For example,
- reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 50% by 2030.
- achieving zero waste to landfill in our global production operations by 2030.
Once the strategy and commitments are in place, the question is, “How do we achieve them, and what tactics (ESG initiatives) do we launch?”
PART 2: THE ESG JOURNEY
To define the list of strategic initiatives the company wants to launch, it must clearly understand its ESG commitments and to which stage of the ESG journey it contributes. Let’s take a closer look at the four stages and their specifics.
BECOME TRANSPARENT
build your ESG inventory
At this stage, businesses recognize the need to build a solid ESG foundation, platform, and inventory, and start tracking its impact. The inventory covers business functions and operations, suppliers, vendor and partner management, and processes and relationships. While building the inventory, the business will need answers to a few specific questions:
- How do we build an ESG process and data foundation? How do we understand our negative impact? What impact-related metrics should we monitor?
- How do we track and report our progress and impact?
- How do we define ESG risks and targets? How do we create an action plan?
Here’s an exemplary service offering designed to assist our clients in developing their ESG programs:
MITIGATE AND REDUCE
launch mitigating and reducing ESG initiatives
The organization has already built its process and data foundation, now it’s time to move to the next stage: mitigating and reducing. When companies find themselves at this stage, they clearly understand the harmful impact they have on the environment and people. They start building strategies to mitigate the risks for the company and to reduce the level of negative impact. The business must honestly answer the following questions while designing an actionable roadmap of ESG initiatives:
- How can we develop initiatives to mitigate ESG risks?
- How can we create initiatives to avoid or reduce our negative impact?
Check out a few of our customer projects that aim to mitigate and reduce ESG risks:
Emission Data Management in Oil and Gas
Automating Visual Inspection of Offshore Facilities
Data-Driven Asset Management for Energy
Optimize Oil and Gas Production With Smart Artificial Lift Solutions
INNOVATE AND COMPENSATE
incorporate product innovation into your DNA and build positive outcome solutions
At this point, the company has reached its limit of potential optimizations, reduction programs, and predictive solutions. They must innovate to stay attractive to their customers from a sustainability perspective. Previous innovation goals might vanish as new ESG solutions come into play. At the same time, the company must come up with new ideas that generate positive outcomes. For example, it could build a digital twin of a warehouse with simulations for optimal warehouse management solutions and decisions, as well as appropriate resource planning, both natural and human resources. The digital twin simulation helps save resources and avoid any negative impact from real-world operations just by making the simulation happen in a virtual setting. Here are some questions to address during this stage:
- How do we move toward net-zero and long-term sustainable growth targets?
- How do we measure the convertible positive impact of the solutions to compensate for the harm we do?
Enjoy some cutting-edge innovations from SoftServe research and development (R&D):
The Power of Simulation: Visibility and Compounding Efficiency
Top European Food Producer Explores Robotics and Automation on the Vertical Farm
CONTRIBUTE TO POSITIVE CHANGE
At this stage, organizations will begin contributing to ambitious worldwide programs to show their proactive position in saving the world for future generations or addressing poverty and hunger. They will launch ESG initiatives with local communities or as global programs. While creating the plan, they’ll consider:
- How do we create ESG initiatives to considerably contribute to the worldwide sustainable programs that serve people and the planet?
As companies take on parallel initiatives contributing to different stages of the ESG journey, they will need to keep track of and calculate the impact of the initiatives already happening. Allowing them to answer questions about their impact on the environment and people, either negative or positive.
A recent study by Ernst & Young LLP C-suite Insights: Sustainability and ESG Trends Index, highlights the sustainability and ESG elements organizations are focusing on. The study includes responses from the C-suite across several Fortune 1000 companies.
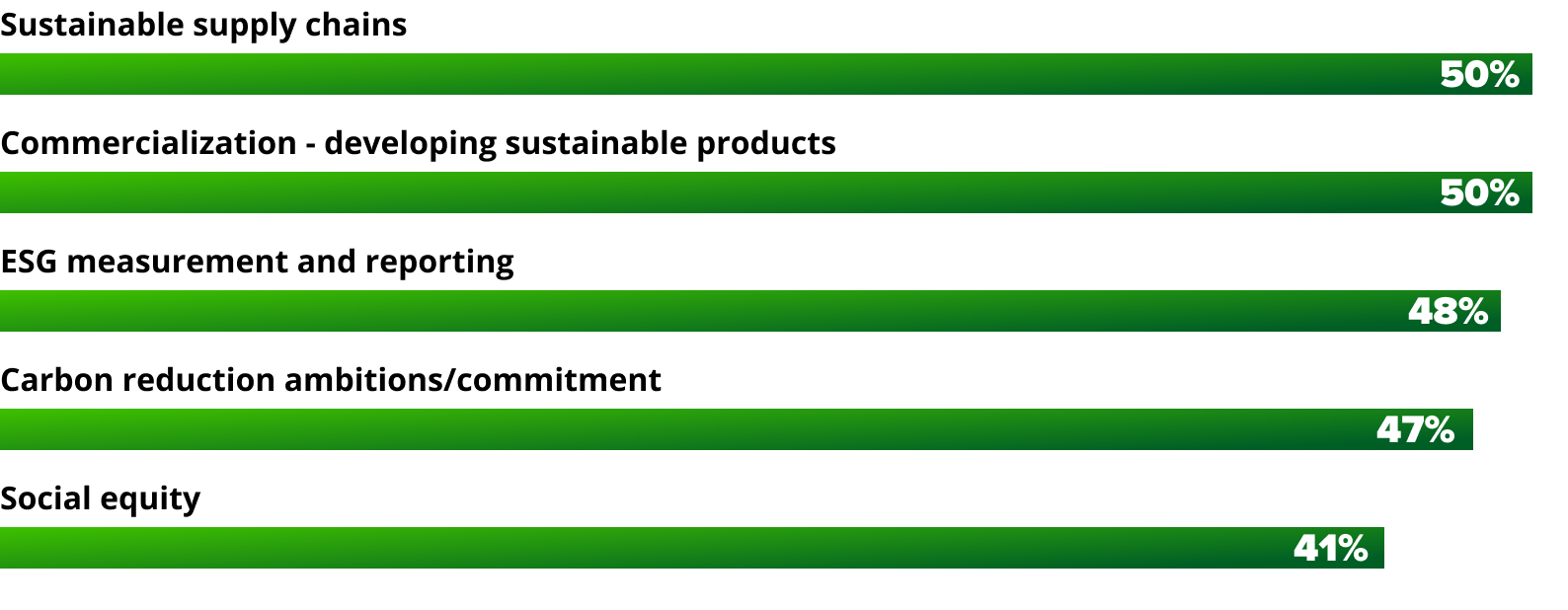

All the mentioned ESG elements contribute to one or more stages of the ESG journey and highlight the significance of considering impact as the primary driver for ESG initiatives.
These initiatives must be adopted across the business and considered in your digital transformation roadmap. Digital will be the backbone of the changes, while change management will be the glue that ensures adoption across the entire enterprise.
For advice on adopting ESG initiatives, check out SoftServe’s Digital Strategy, Innovation, and Change Management Practices.
As organizations initiate their ESG programs, it’s important to:
- Align them with business and digital strategies
- Establish proper process and data foundations
- Build direct and indirect inventories across the value chain
- Track emissions and report on their progress toward defined ESG targets
Digital partners like SoftServe offer support and help build trust throughout the journey.
Here are some additional SoftServe ESG resources:
Data-Driven Energy Optimization: Making Cuts Without Sacrifices
Deploying Composite AI and Historical Know-How for Energy Management
Expanding Your Horizon: Becoming an Early Innovator

Every day, we leverage our multi-domain specializations in energy, oil and gas, manufacturing, agriculture, high tech, retail, and healthcare to evaluate ESG impact into quantifiable, actionable data.
SoftServe offers the solutions and expertise that can help you reach your ESG market goals and meet government reporting requirements. We've been around since 1993, so our experience in finding data analysis and optimum solutions runs deep!

